The least common multiple (often shortened to LCM) is a number that is a multiple of two or more whole numbers. It is called “least” because it is the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly. For example, the LCM of 3 and 4 is 12, because 12 is the smallest number that both 3 and 4 divide into without leaving a remainder.
Multiples are numbers we get when we multiply a number by whole numbers like 1, 2, 3, and so on. For example, the multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, and so on. When we look for the least common multiple of two numbers, we find the first number that appears in both lists of multiples. This helps us find a shared pattern between numbers.
There are several ways to find the LCM. One simple way is by listing multiples. For example, to find the LCM of 5 and 6, we list their multiples: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 6, 12, 18, 24, 30. The first number that appears in both lists is 30, so the LCM is 30. Another method uses prime factorization. This means breaking numbers into their smallest prime factors and then multiplying all the primes needed to cover both numbers. For example, 12 = 2 × 2 × 3, and 18 = 2 × 3 × 3, so the LCM is 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 = 36.
The LCM is very useful in math, especially when working with fractions. To add or compare fractions with different denominators, we use their least common multiple to find a common denominator. For example, to add 1/3 and 1/4, we find the LCM of 3 and 4, which is 12. We then make both fractions have 12 as the denominator, which allows us to add them easily.
The LCM also appears in real-life situations that involve patterns or timing. For instance, if two traffic lights turn red every 45 seconds and 60 seconds, the LCM (180 seconds) tells us when they will turn red at the same time again. This concept helps in planning schedules, repeating events, or synchronizing cycles.
Finding the LCM helps us understand relationships between numbers. It shows how different quantities can work together through multiples and patterns. Learning to find the least common multiple is an important skill in arithmetic that prepares students for higher-level math like algebra and problem solving.
Least common multiple
Level
readlittle.com
The smallest shared multiple of numbers
What We Can Learn
- The least common multiple (LCM) is the smallest number shared by given numbers.
- It can be found by listing multiples or using prime factorization.
- The LCM helps when adding or comparing fractions with different denominators.
- LCMs appear in patterns, timing, and real-world number relationships.
Related Reads

Rational number
Numbers written as a fraction
Prime number
Numbers with only two factors

Divisibility rule
Shortcuts for spotting factors

Decimal
Base-ten numbers with fractional parts
Percentage
Comparing amounts per hundred
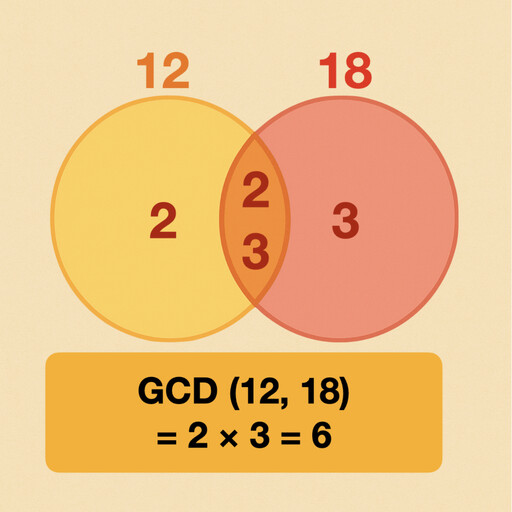
Greatest common divisor
The largest number dividing others evenly

Mathematics
The universal language of numbers and patterns