The tongue is a soft, flexible organ found inside the mouth. It is made mostly of muscle. The tongue has several important roles in the body. It helps with tasting food, moving food while eating, and forming sounds during speech. The tongue works closely with the teeth, lips, and throat. Even though it is small, it is active almost all the time.
The surface of the tongue is covered with many tiny bumps. These bumps are called papillae. Some papillae contain taste buds. Taste buds are small groups of cells that can sense flavors. Humans can sense several basic tastes, such as sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami. Umami is a taste linked to savory foods like meat or soup. When food touches the tongue, taste buds send signals to the brain. The brain then identifies the taste.
The tongue also helps with eating. When a person chews food, the tongue moves it around the mouth. This helps mix food with saliva. Saliva is a watery liquid made by glands in the mouth. Saliva softens food and begins breaking it down. The tongue then pushes the food to the back of the mouth so it can be swallowed safely.
Speech is another important function of the tongue. The tongue changes shape and position to help make sounds. Many spoken sounds depend on how the tongue touches the teeth, roof of the mouth, or throat. Without the tongue, clear speech would be very difficult. The tongue works together with airflow from the lungs to form words.
The tongue is connected to the body by nerves and blood vessels. Nerves carry taste signals and movement instructions between the tongue and the brain. Blood vessels bring oxygen and nutrients to keep the tongue healthy. The tongue can heal quickly if it is injured because it has a strong blood supply.
In humans, the tongue stays moist most of the time. This helps taste buds work well and allows smooth movement. The tongue is always moving slightly, even when a person is resting. Through its roles in taste, eating, and speech, the tongue supports many daily activities.
Tongue
Level
readlittle.com
Muscle organ for taste and speech
What We Can Learn
- The tongue is a muscle inside the mouth
- It helps with taste, eating, and speech
- Taste buds on the tongue send signals to the brain
- The tongue moves food for chewing and swallowing
Related Reads
Ear
Organ used for hearing and balance
Nose
Organ used for smell and breathing
Eye
Organ used for seeing light
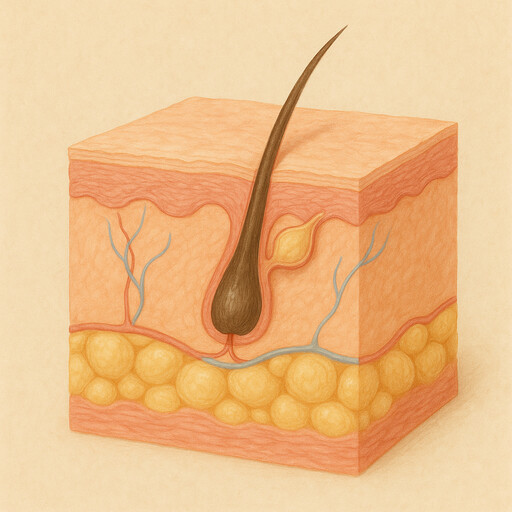
Skin
Outer covering of the human body

Turtle
Shell-covered travelers of land and sea

Horse
Powerful partners with steady hooves

Giraffe
Tall guardians of the savanna
Anatomy
Study of body structure in living things

Tyrannosaurus
Large carnivorous dinosaur of late Cretaceous

Jellyfish
Drifting cnidarians with stinging tentacles
Joint
Meeting place of two or more bones
Spleen
Blood filter and immune warehouse