The respiratory system is the group of organs that helps humans and animals breathe. breathing is one of the most important life processes because it provides the body with oxygen, which cells need to make energy. The system also removes carbon dioxide, a waste gas produced when the body uses energy. Without this system, the body would not survive for more than a few minutes.
The process of breathing starts when air enters through the nose or mouth. The air then passes through the trachea, also called the windpipe, which divides into two bronchi. Each bronchus leads to a lung. Inside the lungs, the bronchi branch into smaller tubes called bronchioles, ending in tiny air sacs known as alveoli. These alveoli are surrounded by small blood vessels, or capillaries, where oxygen moves into the blood and carbon dioxide moves out to be exhaled.
The act of breathing is controlled by a muscle called the diaphragm. It sits below the lungs and moves up and down to help draw air in and push it out. When the diaphragm contracts, the chest expands and air flows into the lungs. When it relaxes, the chest gets smaller and air is pushed out. This constant movement keeps oxygen entering and carbon dioxide leaving the body all day and night, even while sleeping.
The respiratory system works closely with the circulatory system. After oxygen enters the blood in the lungs, the heart pumps it to every part of the body. The cells use oxygen to make energy, and the waste gas carbon dioxide travels back through the blood to the lungs to be exhaled. This cycle repeats thousands of times every day.
Besides breathing, the respiratory system also helps protect the body. The nose filters dust and germs using small hairs and mucus. Sneezing and coughing are ways the system clears irritants out of the airways. Talking, singing, and laughing are also made possible by air moving through the vocal cords in the throat.
Keeping the respiratory system healthy is very important. Clean air, regular exercise, and not smoking help the lungs stay strong. Breathing fresh air outdoors and staying away from pollution can also protect this system. A healthy respiratory system gives the body the energy it needs to grow, move, and stay active.
Respiratory system
Level
readlittle.com
How the body breathes and gets oxygen
What We Can Learn
- The respiratory system helps us breathe and get oxygen.
- Air travels through the nose, trachea, and lungs to reach tiny alveoli.
- The diaphragm helps air move in and out of the lungs.
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged to keep the body alive.
Related Reads
Nose
Organ used for smell and breathing

Pet
Animal companions in human homes
Joint
Meeting place of two or more bones

Muscle
Tissue that helps bodies move
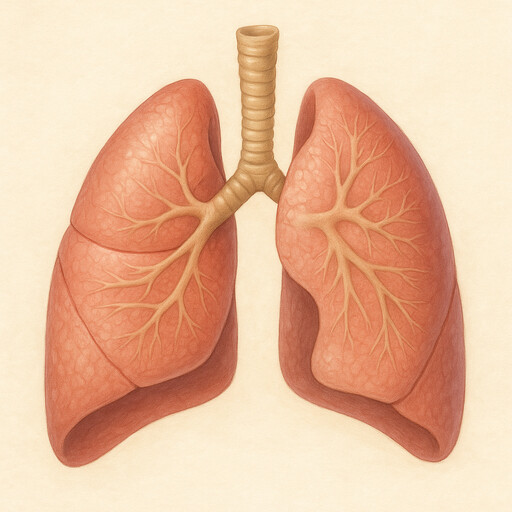
Lung
Breathing partner of the heart
Esophagus
Muscular tube guiding food to the stomach
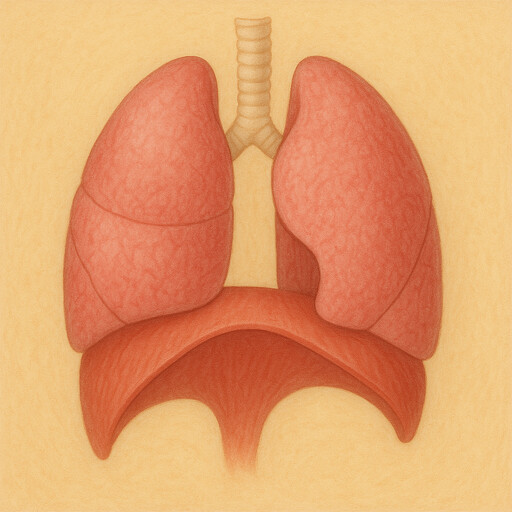
Diaphragm
Breathing muscle beneath the lungs

Pancreas
Dual-role gland for digestion and hormones
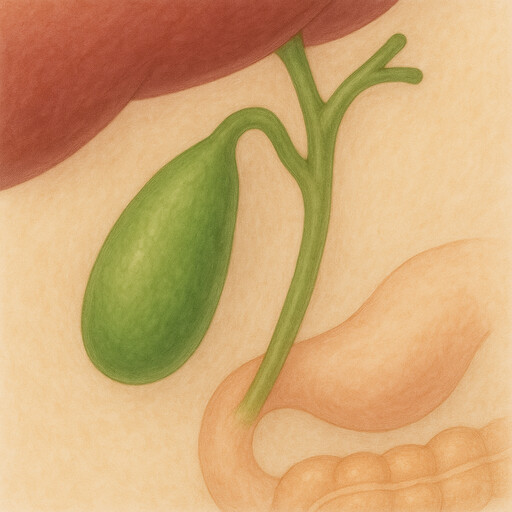
Gallbladder
Bile reservoir aiding fat digestion
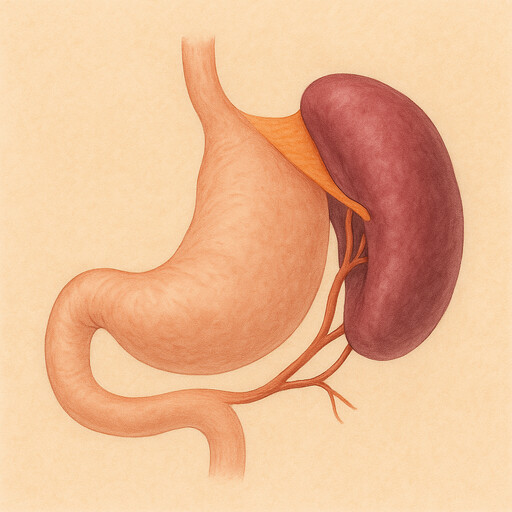
Spleen
Blood filter and immune warehouse
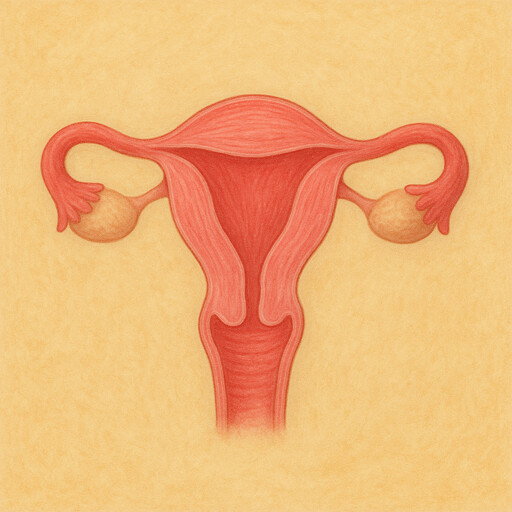
Ovary
Egg-producing gland in the pelvis
Testis
Sperm- and hormone-producing gland