Jupiter is the fifth planet from the sun and the largest planet in the solar-system. It is more than 11 times wider than earth and has a strong influence on other planets because of its size and gravity. Jupiter is named after the king of the gods in Roman mythology. It is often called a gas giant because it is made mostly of hydrogen and helium, with no solid surface like Earth.
Jupiter’s most noticeable feature is the Great Red Spot, a huge storm that has been blowing for hundreds of years. This storm is so large that it could fit several Earths inside it. Jupiter’s atmosphere is full of colorful clouds and stripes, caused by strong winds moving in different directions at very high speeds. These clouds are made of ammonia and other gases that reflect sunlight and give the planet its banded appearance.
A day on Jupiter is the shortest of any planet in the Solar System, lasting only about 10 Earth hours. This means it spins very quickly on its axis. However, because it is far from the Sun, a year on Jupiter takes about 12 Earth years. Its fast rotation causes its middle to bulge outward, making it slightly flattened at the poles.
Jupiter has a very strong magnetic field and gives off more heat than it receives from the Sun. It also has thin rings made of dust, though they are much fainter than the bright rings of saturn. The planet has at least 95 moons, and four of them are large enough to be seen with small telescopes. These are called the Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System and even bigger than the planet mercury.
The atmosphere and weather on Jupiter are extreme. The winds can reach speeds of more than 600 kilometers per hour, and lightning storms have been observed by spacecraft. Jupiter’s size and gravity help protect the inner planets, including Earth, by attracting or deflecting comets and asteroids that could otherwise hit them.
Many spacecraft have studied Jupiter, such as Pioneer, Voyager, Galileo, and Juno. The Juno spacecraft, which began orbiting Jupiter in 2016, continues to send back new information about its structure, magnetic field, and clouds. Studying Jupiter helps scientists understand how giant planets form and how the Solar System developed billions of years ago.
Jupiter
Level
readlittle.com
The largest planet in the Solar System
What We Can Learn
- Jupiter is the fifth and largest planet from the Sun.
- It is a gas giant with no solid surface.
- It has many moons, including the four large Galilean moons.
- The Great Red Spot is a giant storm that has lasted for centuries.
Related Reads
Apollo 11
First human landing on the Moon

Neil Armstrong
First human to walk on the Moon

Apollo 8
First human mission to orbit the Moon

Gravity
Force that pulls objects together

Nicolaus Copernicus
Astronomer who placed the Sun at center

Johannes Kepler
Astronomer who described planet motion

Galileo Galilei
Early observer of the skies

Exoplanet
Planets beyond our solar system
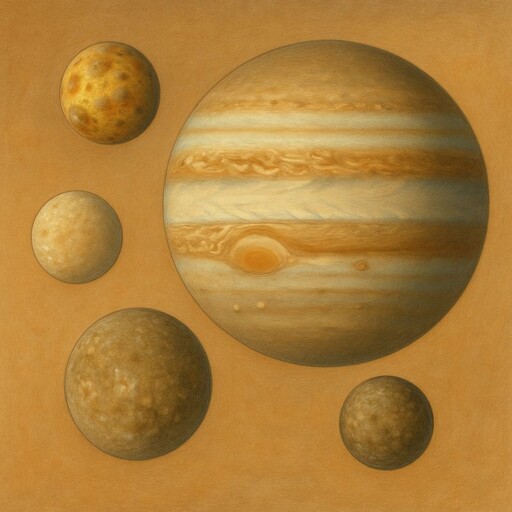

Galilean moons
Four large moons of Jupiter

Asteroid belt
Region of rocky bodies in space

Aurora
Colorful lights in Earth’s sky
Orbit
The path of one object around another in space