Hormones are special chemicals that the body makes to help control and coordinate many different activities. They are produced by glands, which are small organs found in different parts of the body. Hormones travel through the blood to reach other parts of the body, where they send messages to organs, tissues, and cells. These messages help the body grow, use energy, and stay balanced.
The system that makes and uses hormones is called the endocrine system. Some of the major glands in this system include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pancreas. Each gland releases its own types of hormones. For example, the pancreas produces insulin, which helps control the amount of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gland makes hormones that control how fast the body uses energy.
Hormones are very powerful, and even a small amount can cause big changes in the body. They help control growth and development, such as how fast a child grows or when puberty begins. They also affect mood, sleep, hunger, and the body’s response to stress. Because hormones are always working, they help keep the body’s systems balanced and steady. This state of balance is called homeostasis.
Different hormones have different jobs. For example, adrenaline helps the body react quickly when it faces danger by increasing heart rate and energy. Estrogen and testosterone are hormones that help control growth and development of the reproductive systems. Melatonin helps control sleep by signaling the body when it is time to rest.
Sometimes the body makes too much or too little of a hormone. This can cause problems called hormonal imbalances. Doctors can test hormone levels to find out what is wrong and may give medicine to help balance them again. A healthy lifestyle, including good nutrition and enough sleep, helps the endocrine system work properly.
Overall, hormones are the body’s tiny messengers that keep everything working together smoothly. They help people grow, think, and respond to the world in many ways every day.
Hormone
Level
readlittle.com
Natural chemical messengers in the body
What We Can Learn
- Hormones are natural chemicals made by glands in the body.
- They act as messengers to control and coordinate body functions.
- The endocrine system produces and manages different hormones.
- Balanced hormone levels help keep the body healthy and stable.
Related Reads

Shrew
Tiny insectivores with turbo metabolisms
Metabolism
How living things use energy

Insect
Six-legged masters of adaptation

Seashell
Hard homes left by marine mollusks
Liver
Chemical factory and guardian

Pancreas
Dual-role gland for digestion and hormones
Thyroid gland
Butterfly-shaped regulator of metabolism
Diet
The food people and animals eat

Health
The state of body and mind well-being

Metamorphosis
The change of form in animals

Skull
The hard bone that protects the brain
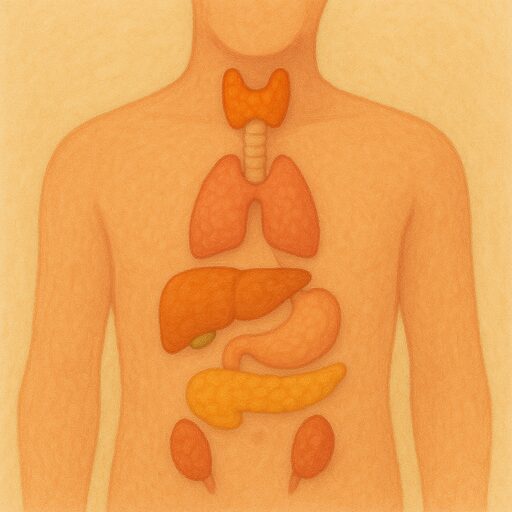
Endocrine system
The body's chemical messenger network