NASA is the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. It is a civilian agency of the United States government. NASA was created in 1958, during a time when several countries were beginning to explore space. The agency studies space beyond Earth, the planet itself, and flight through the atmosphere. NASA plans missions, builds spacecraft, and operates research centers. It works with astronauts, engineers, scientists, and pilots. NASA does not control the military. Its activities are focused on research, exploration, and testing.
NASA was formed after a period called the Space Race. The Space Race was a time of competition between the United States and the Soviet Union to achieve spaceflight goals. Before NASA existed, space research in the United States was led by a group called the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, or NACA. When the Soviet Union launched the satellite Sputnik 1 in 1957, the United States decided to create a larger space agency. President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed the law that created NASA. The new agency combined earlier research programs and began planning missions into space.
One of NASA’s earliest goals was to send humans into space. The first program was Project Mercury. It tested whether humans could survive spaceflight. This was followed by the Gemini program, which focused on longer flights and learning how spacecraft could meet and connect in space. This process is called docking. These programs prepared NASA for the Apollo program. Apollo missions were designed to land humans on the Moon and return them safely to Earth. In 1969, the Apollo 11 mission achieved this goal. Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin walked on the Moon, while Michael Collins orbited above.
After the Apollo program, NASA continued human spaceflight with new systems. In 1981, NASA launched the first Space Shuttle. The Space Shuttle was a reusable spacecraft, meaning parts of it could be used again. Shuttles carried astronauts, satellites, and equipment into orbit. They also helped build the International Space Station, or ISS. The ISS is a large laboratory in space where astronauts from different countries live and work. NASA has operated missions to the ISS for many years, sending crews and supplies on regular flights.
NASA also carries out many robotic missions. These missions use unmanned spacecraft, which are vehicles without people on board. Robotic probes have been sent to study the Moon, Mars, Venus, and the outer planets. Mars rovers, such as Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance, are robotic vehicles that move across the surface of Mars. They study rocks, soil, and weather. NASA also operates space telescopes. A telescope is an instrument that gathers light to observe distant objects. The Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope observe stars, galaxies, and planets far beyond Earth.
In addition to space exploration, NASA studies Earth and flight. Earth-observing satellites track weather, oceans, ice, and land. These satellites collect data over long periods. NASA also researches aeronautics, which is the science of flight within Earth’s atmosphere. This work includes studying aircraft design, safety, and noise. NASA has several research centers across the United States, including the Kennedy Space Center in Florida and the Johnson Space Center in Texas. Today, NASA continues to plan missions, operate spacecraft, and collect data about space and Earth.
NASA
Level
readlittle.com
United States space agency
What We Can Learn
- NASA is the space agency of the United States
- It was created in 1958 during the Space Race
- NASA led human missions to the Moon
- The agency runs human and robotic space missions
Related Reads
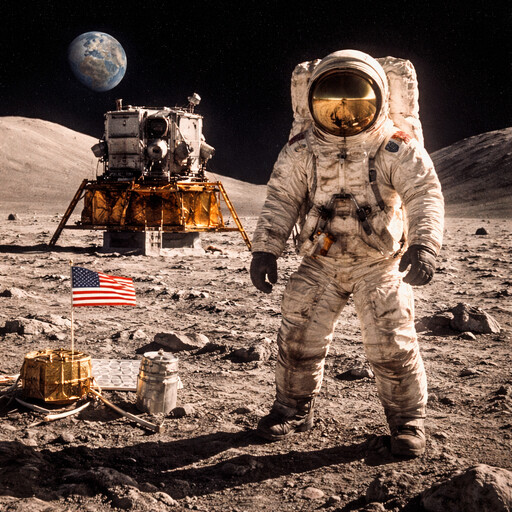
Apollo 11
First human landing on the Moon
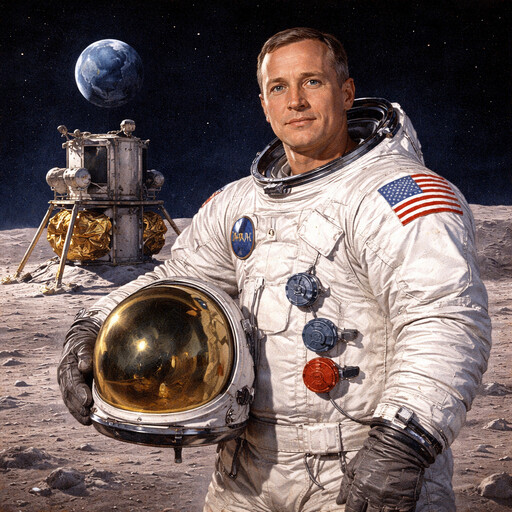

Neil Armstrong
First human to walk on the Moon
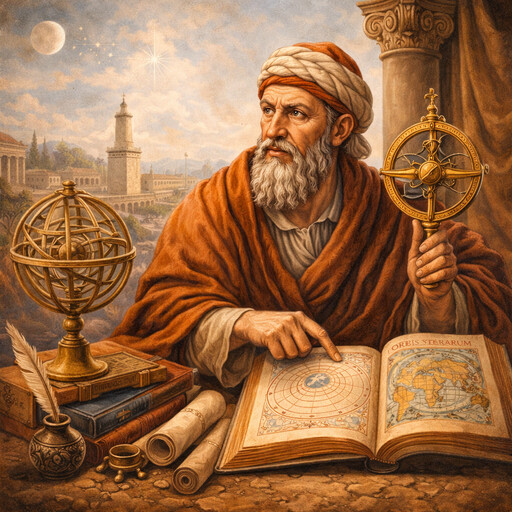

Ptolemy
Ancient scholar of astronomy and geography
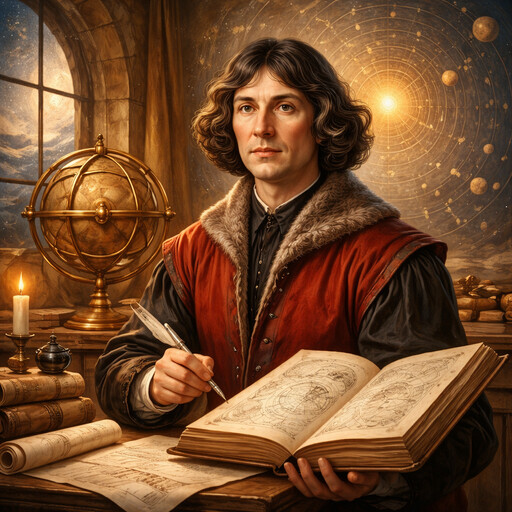

Nicolaus Copernicus
Astronomer who placed the Sun at center

Johannes Kepler
Astronomer who described planet motion

Hubble Space Telescope
Space telescope orbiting Earth

Supernova
Powerful explosion of a dying star

Galileo Galilei
Early observer of the skies

Nebula
Clouds of gas and dust in space

Exoplanet
Planets beyond our solar system

Galilean moons
Four large moons of Jupiter

Atacama Desert
Chile's hyper-arid science frontier